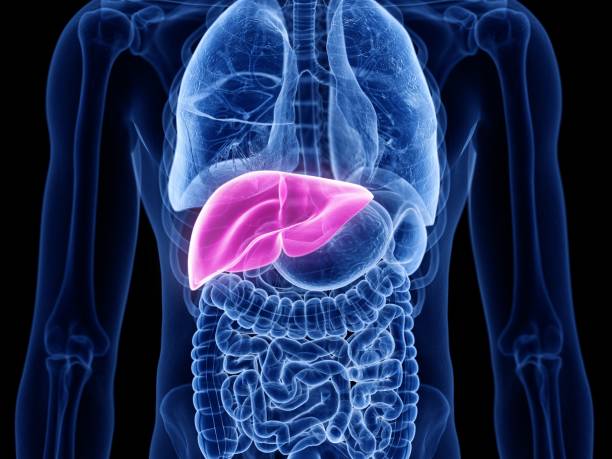
The liver is one of the most vital organs in the body, performing essential functions that keep us healthy. It’s a powerhouse of activity, working tirelessly to ensure our body operates smoothly. Let’s delve into its roles, the diseases that can affect it, and tips for maintaining liver health.
Functions of the Liver
Detoxification
- Cleansing the Blood: The liver detoxifies harmful substances, such as drugs and alcohol, from the blood.
- Breaking Down Toxins: It converts ammonia, a byproduct of protein metabolism, into urea, which is then excreted in urine.
Metabolism
- Fat Metabolism: The liver metabolizes fats and produces bile to aid in the digestion and absorption of fats.
- Carbohydrate Metabolism: It helps regulate blood sugar levels by converting excess glucose into glycogen for storage and breaking it down when needed.
- Protein Metabolism: The liver synthesizes essential proteins, including those necessary for blood clotting.
Storage
- Vitamin and Mineral Storage: The liver stores vitamins A, D, E, K, and B12, as well as minerals like iron and copper.
Bile Production
- Digestion: The liver produces bile, which is stored in the gallbladder and released into the small intestine to aid in the digestion and absorption of fats.
Common Liver Diseases
Hepatitis
- Types: Hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E are viral infections that cause liver inflammation.
- Transmission: Hepatitis can be transmitted through contaminated food and water, blood, and other bodily fluids.
Fatty Liver Disease
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Accumulation of fat in the liver not caused by alcohol consumption.
- Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Fat accumulation due to excessive alcohol intake.
Cirrhosis
- Scarring: Chronic liver damage leads to scarring (fibrosis) and impaired liver function.
- Causes: Commonly caused by chronic hepatitis and long-term alcohol abuse.
Liver Cancer
- Types: Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most common type of primary liver cancer.
- Risk Factors: Chronic hepatitis infection, cirrhosis, and certain genetic disorders increase the risk.
Tips for a Healthy Liver
Limit Alcohol Consumption

- Moderation: Avoid excessive alcohol intake to prevent liver damage. For men, this means no more than two drinks per day, and for women, no more than one.
Healthy Diet
- Balanced Nutrition: Eat a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Avoid Processed Foods: Reduce intake of high-fat, high-sugar, and highly processed foods.
Stay Hydrated
- Drink Water: Hydration is essential for overall health and helps the liver function properly.
Avoid Toxins
- Reduce Exposure: Limit exposure to environmental toxins, chemicals, and avoid recreational drug use.
Regular Exercise
- Physical Activity: Engage in regular physical activity to maintain a healthy weight and support liver function.
Vaccination
- Hepatitis Vaccines: Get vaccinated against hepatitis A and B to protect your liver from these infections.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Symptoms to Watch For
- Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes.
- Abdominal Pain: Persistent pain in the upper right side of the abdomen.
- Fatigue: Unexplained chronic fatigue and weakness.
- Swelling: Swelling in the legs and abdomen.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Persistent nausea and vomiting.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider promptly. Early detection and treatment of liver conditions can significantly improve outcomes.
Conclusion: Celebrate Your Liver’s Hard Work
The liver is truly an unsung hero, performing numerous vital functions that keep our bodies healthy. By taking proactive steps to support its health—such as limiting alcohol, eating a balanced diet, staying hydrated, avoiding toxins, exercising regularly, and getting vaccinated—we can ensure our liver continues to function optimally. Celebrate your liver’s hard work by making healthy lifestyle choices and seeking medical advice when necessary. Your liver will thank you!