Chronic liver diseases can significantly impact your health, but with proper management, you can improve your quality of life. This guide provides a comprehensive understanding of chronic liver diseases, their symptoms, and effective management strategies to help you lead a healthier life.
Understanding Chronic Liver Diseases
Chronic liver diseases encompass a range of conditions that cause long-term damage to the liver. Some of the most common chronic liver diseases include:
- Hepatitis: An inflammation of the liver caused by viral infections (hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E), excessive alcohol consumption, or autoimmune diseases.
- Cirrhosis: A late-stage liver disease characterized by scarring (fibrosis) of the liver tissue, which can result from chronic hepatitis, alcohol abuse, or other liver diseases.
- Fatty Liver Disease: Accumulation of fat in liver cells, often linked to obesity, diabetes, and excessive alcohol consumption. It includes non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD).
Recognizing the Symptoms
Early detection and management of chronic liver diseases are crucial for preventing severe complications. Common symptoms to watch for include:
- Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes, indicating elevated bilirubin levels in the blood.
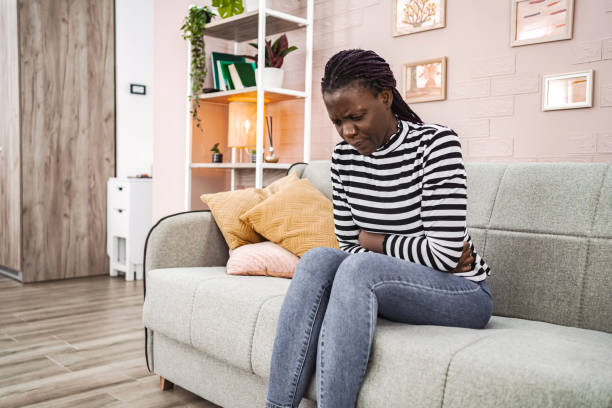

- Abdominal Pain and Swelling: Discomfort or pain in the upper right side of the abdomen, along with swelling due to fluid accumulation (ascites).
- Chronic Fatigue: Persistent tiredness and weakness.
- Nausea or Vomiting: Gastrointestinal distress, including frequent nausea and vomiting.
- Loss of Appetite: Decreased desire to eat, leading to unintentional weight loss.
Management Strategies
Managing chronic liver diseases involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medication adherence, and regular medical monitoring. Here are some effective strategies:
Healthy Diet

- Balanced Nutrition: Consume a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Avoid foods high in saturated fats, sugar, and salt.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to help your liver function efficiently.
- Limit Processed Foods: Avoid processed and fried foods, which can contribute to liver damage.
Avoid Alcohol
- Alcohol Abstinence: Refrain from alcohol consumption as it can exacerbate liver damage and accelerate the progression of liver diseases.
- Support Groups: Consider joining support groups or seeking counseling to help with alcohol cessation if needed.
Regular Exercise
- Physical Activity: Engage in moderate-intensity exercise, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, for at least 150 minutes per week. Exercise helps maintain a healthy weight and reduces fat accumulation in the liver.
- Strength Training: Incorporate strength training exercises to build muscle mass and improve overall health.
Medication Adherence

- Follow Prescriptions: Take medications as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Medications can help manage symptoms, reduce liver inflammation, and slow disease progression.
- Regular Monitoring: Keep track of your medication schedule and attend follow-up appointments for dose adjustments and monitoring.
Vaccination
- Hepatitis Vaccination: Get vaccinated against hepatitis A and B to prevent viral hepatitis infections, which can further damage the liver.
- Flu and Pneumonia Vaccines: These vaccinations are also recommended to protect against infections that can strain the liver.
Regular Checkups
- Medical Checkups: Schedule regular appointments with your healthcare provider to monitor liver function and disease progression. Regular blood tests, imaging studies, and liver biopsies may be necessary.
- Early Intervention: Early detection of complications, such as liver cancer or portal hypertension, allows for timely treatment and better outcomes.
When to Seek Help
It’s crucial to seek medical advice if you experience symptoms of liver disease or if your condition worsens. Consult your healthcare provider if you notice:
- Increased Jaundice: Worsening yellowing of the skin and eyes.
- Severe Abdominal Pain: Intense pain in the upper right abdomen.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Significant weight loss without a change in diet or exercise.
- Changes in Mental State: Confusion, difficulty concentrating, or other cognitive changes.
- Signs of Bleeding: Unexplained bruising or bleeding, which may indicate liver dysfunction affecting blood clotting.
Conclusion
Managing chronic liver diseases requires a proactive approach that includes healthy lifestyle choices, medication adherence, and regular medical monitoring. By recognizing the symptoms early and implementing effective management strategies, you can improve your quality of life and reduce the risk of severe complications. Consult your healthcare provider regularly and take steps to support your liver health, ensuring a better, healthier future.